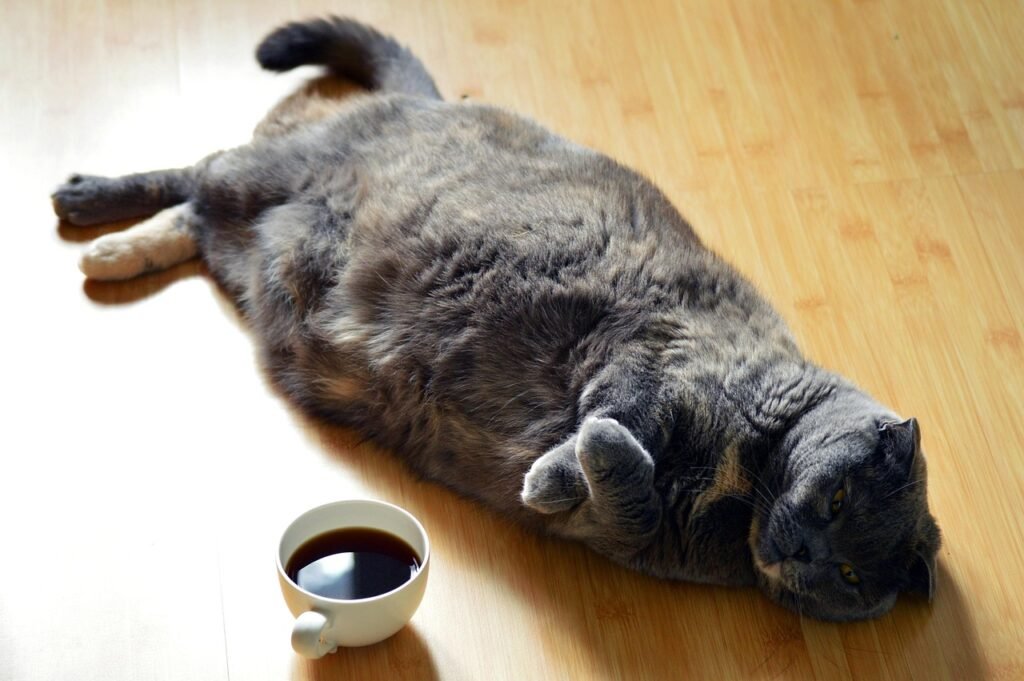
Feline obesity is a growing concern among pet owners and veterinarians alike, as it poses significant health risks to pets. Defined as an excess accumulation of body fat, obesity can lead to a myriad of health complications, including diabetes, arthritis, and cardiovascular diseases. The prevalence of obesity in domestic cats has increased dramatically over the past few decades, with studies indicating that nearly 60% are classified as overweight or obese.
This alarming trend not only affects the physical well-being of pets but also their overall quality of life, making it imperative for owners to understand the dangers associated with this condition. The health risks associated with feline obesity are multifaceted. For instance, overweight pets are more susceptible to developing diabetes mellitus, a condition that can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Additionally, excess weight places undue stress on a pet’s joints, increasing the likelihood of arthritis and mobility issues. Furthermore, obesity can contribute to respiratory problems and a decreased ability to regulate body temperature, which can be particularly dangerous in extreme weather conditions. Recognizing these risks is crucial for owners who wish to ensure their pets lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Key Takeaways
- Feline obesity poses serious health risks for cats, including diabetes, arthritis, and decreased lifespan.
- Causes of feline obesity can include overfeeding, lack of exercise, and genetic predisposition.
- Obesity can significantly impact a cat’s quality of life, leading to decreased mobility and increased risk of other health issues.
- Preventing and managing feline obesity involves a combination of diet control, portion management, and regular exercise.
- Seeking veterinary care and creating a healthy environment are crucial steps in combatting feline obesity and promoting a cat’s overall well-bein
The Health Risks of Feline Obesity
The health implications of obesity extend beyond mere aesthetics; they can significantly impact a pet’s longevity and quality of life. One of the most concerning risks is the development of diabetes, which occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin due to excessive fat accumulation. This condition not only requires lifelong management but can also lead to severe complications such as ketoacidosis, a potentially life-threatening state.
Moreover, overweight pets are at a higher risk for hepatic lipidosis, a serious liver condition that can arise when a pet stops eating due to obesity-related health issues. In addition to metabolic disorders, excess weight can exacerbate pre-existing health conditions. For example, pets with heart disease may experience worsened symptoms due to excess weight, while those with kidney disease may find their condition deteriorating more rapidly.
The increased risk of certain cancers in obese pets further underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy weight. By understanding these health risks, owners can take proactive steps to prevent obesity and its associated complications.
Identifying the Causes of Feline Obesity
Understanding the root causes of obesity is essential for effective prevention and management. One primary factor contributing to weight gain is overfeeding. Many owners may unknowingly provide excessive portions or high-calorie treats, leading to an imbalance between caloric intake and energy expenditure.
Additionally, the availability of calorie-dense commercial foods can make it easy for pets to consume more calories than they need. It is crucial for owners to be aware of portion sizes and to follow feeding guidelines provided by veterinarians or pet food manufacturers. Another significant contributor to obesity is a sedentary lifestyle.
Unlike their wild counterparts, domestic pets often lack opportunities for physical activity due to indoor living conditions. This inactivity can lead to weight gain over time, especially if combined with overfeeding. Environmental factors such as limited space for play or lack of stimulating toys can further exacerbate this issue.
By identifying these causes, owners can implement changes that promote healthier habits for their companions.
The Impact of Obesity on a Cat’s Quality of Life
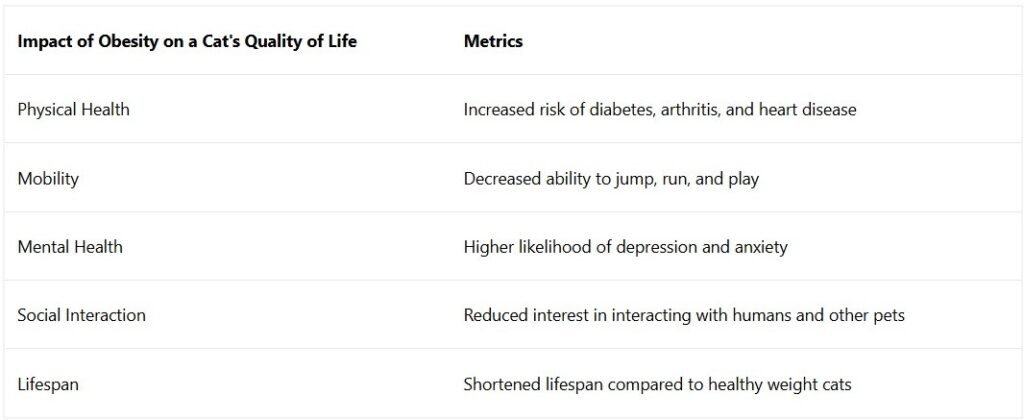
Obesity can severely diminish a cat’s quality of life in various ways. Physically, overweight cats may struggle with mobility issues, making it difficult for them to engage in normal activities such as climbing, jumping, or grooming themselves effectively. This reduced mobility can lead to frustration and decreased social interaction with both humans and other pets in the household.
As a result, an obese cat may become more withdrawn or exhibit behavioral changes that reflect their discomfort. Moreover, the psychological impact of obesity should not be overlooked. Cats that are unable to participate in play or explore their environment may experience boredom and stress, which can further contribute to weight gain in a vicious cycle.
The emotional well-being of a cat is closely tied to its physical health; thus, addressing obesity is not only about managing weight but also about enhancing the overall happiness and fulfillment of the pet’s life.
Strategies for Preventing and Managing Feline Obesity

Preventing and managing obesity requires a multifaceted approach that involves both dietary changes and lifestyle modifications. One effective strategy is to establish a consistent feeding routine that includes measured portions based on the pet’s age, weight, and activity level. Owners should consult with veterinarians to determine appropriate caloric intake and select high-quality food that meets their pet’s nutritional needs without excessive calories.
In addition to dietary management, increasing physical activity is crucial for combating obesity. Engaging in interactive play sessions using toys such as feather wands or laser pointers can stimulate a pet’s natural hunting instincts while providing essential exercise. Creating an enriched environment with climbing structures and scratching posts can also encourage movement and exploration.
By combining these strategies, owners can help their pets achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
The Role of Diet and Exercise in Combatting Feline Obesity
Diet and exercise play pivotal roles in addressing feline obesity effectively. A balanced diet tailored to a cat’s specific needs is fundamental for weight management. Pet owners should prioritize high-protein, low-carbohydrate diets that promote lean muscle mass while minimizing fat accumulation.
Additionally, incorporating wet food into a cat’s diet can help increase hydration and promote satiety without adding excessive calories. Exercise is equally important in combating feline obesity. Regular physical activity not only helps burn calories but also strengthens muscles and improves cardiovascular health.
Owners can encourage exercise by providing various toys that stimulate play or by scheduling daily playtime sessions. Even simple activities like hiding treats around the house can motivate cats to move more throughout the day. By focusing on both diet and exercise, pet owners can create a comprehensive plan for managing their cat’s weight effectively.
Seeking Veterinary Care for Overweight Cats
When it comes to managing feline obesity, seeking veterinary care is an essential step for pet owners. Veterinarians can provide valuable insights into a cat’s specific health needs and help develop tailored weight loss plans that consider any underlying medical conditions. Regular check-ups allow for monitoring progress and adjusting dietary or exercise recommendations as needed.
In some cases, veterinary intervention may include prescription diets designed for weight loss or medications that assist in appetite control. Additionally, veterinarians can educate pet owners about the importance of gradual weight loss rather than rapid changes, which can be detrimental to a cat’s health. By collaborating with veterinary professionals, pet owners can ensure they are taking informed steps toward achieving their cat’s optimal weight.
Creating a Healthy Environment for Feline Weight Management
Creating a healthy environment is crucial for effective feline weight management. This involves not only providing appropriate food portions but also ensuring that cats have access to stimulating activities that promote physical fitness. Owners should consider setting up designated play areas equipped with toys that encourage movement and exploration.
Moreover, reducing access to high-calorie treats and table scraps is vital in maintaining a healthy diet for cats. Instead of relying on food rewards for training or affection, pet owners can use praise or playtime as alternatives that do not contribute to weight gain. By fostering an environment that prioritizes health and activity, pet owners can significantly improve their cats’ chances of achieving and maintaining a healthy weight throughout their lives.
